2AA
Waste Heat Recovery Low Temperature Hot Water Driven Absorption Chiller

2AA Double Lift Low Temperature Hot Water Absorption Chiller
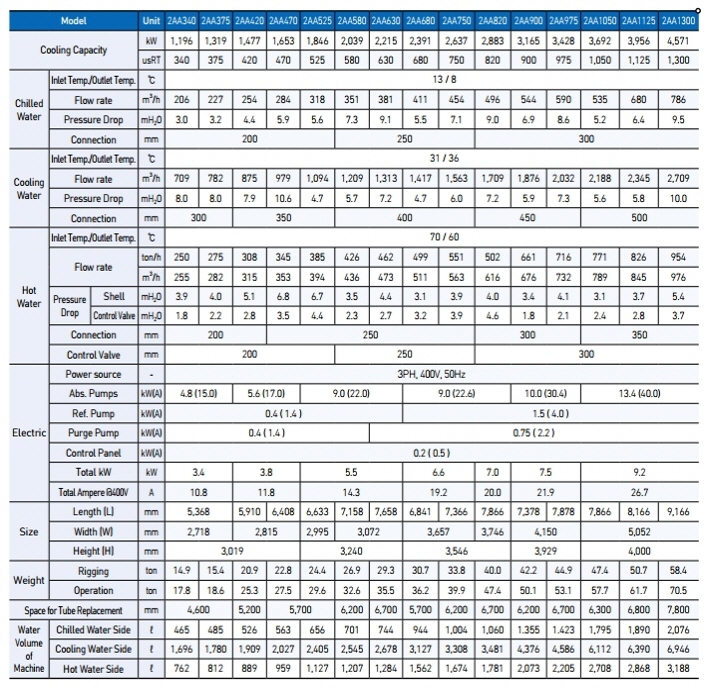
30~2,000RT (105~7,033kW)
Driving Temperature: 70~80℃
Utilizes waste heat from warm water at a low temperature of 70℃
The first double lift refrigeration cycle absorption chiller which can recover heat from low temperature hot water of entering 70℃ and leaving 60℃.
Suitable to 24/7 operation industries
Most benefits to industrial customers who have abundant amount of low temperature waste heat and cooling demand for 24 hours manufacturing operation
Reference
Korea Korea Zinc, Hankuk Paper, YP Zinc
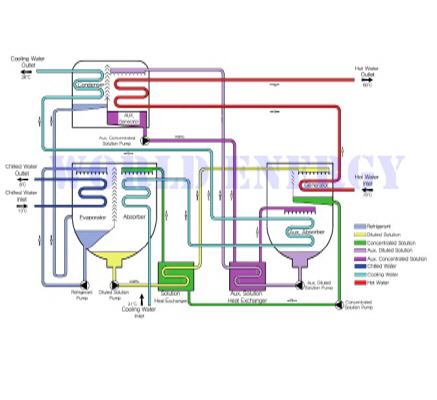
Flow of solution in high-efficiency low-temperature water driven Absorption chillers
Circulation system of absorption liquid
The absorption liquid circulation system is composed of two parts of the main system, and the absorption liquid (diluting solution) absorbed from the main system is pressurized by the solution pump and sent to the generator through the solution heat exchanger. The thick absorbing liquid (concentrated solution) that exits the refrigerant vapor returns to the absorber through the solution heat exchanger.
In the auxiliary system, the absorption liquid (auxiliary solution) absorbed from the generator by the absorption of the refrigerant vapor is discharged from the auxiliary absorber, is pressurized by the solution pump, and is sent to the auxiliary generator through the auxiliary heat exchanger. The absorption liquid (concentrated solution) is returned to the secondary absorber via the auxiliary heat exchanger.
The absorption liquid circulation system is composed of two parts of the main system, and the absorption liquid (diluting solution) absorbed from the main system is pressurized by the solution pump and sent to the generator through the solution heat exchanger. The thick absorbing liquid (concentrated solution) that exits the refrigerant vapor returns to the absorber through the solution heat exchanger.
In the auxiliary system, the absorption liquid (auxiliary solution) absorbed from the generator by the absorption of the refrigerant vapor is discharged from the auxiliary absorber, is pressurized by the solution pump, and is sent to the auxiliary generator through the auxiliary heat exchanger. The absorption liquid (concentrated solution) is returned to the secondary absorber via the auxiliary heat exchanger.
Refrigerant circulation system
In the condenser, the refrigerant vapor from the auxiliary generator is condensed, and the refrigerant liquid flows to the evaporator through the U-tube. In the evaporator, the refrigerant is dispersed to the upper portion of the evaporator by the refrigerant pump, and some evaporated refrigerant vapor is sent to the absorber through the eliminator . The non-evaporated refrigerant liquid accumulates at the bottom of the evaporator and is again distributed to the top of the evaporator by the refrigerant pump.
In the condenser, the refrigerant vapor from the auxiliary generator is condensed, and the refrigerant liquid flows to the evaporator through the U-tube. In the evaporator, the refrigerant is dispersed to the upper portion of the evaporator by the refrigerant pump, and some evaporated refrigerant vapor is sent to the absorber through the eliminator . The non-evaporated refrigerant liquid accumulates at the bottom of the evaporator and is again distributed to the top of the evaporator by the refrigerant pump.
Role of each part
Cold water flows into the evaporator tube and cold water is produced by the evaporation of the refrigerant on the tube surface.
Coolant flows into the absorber tube, absorbing the refrigerant vapor by dispersing the absorbent on the surface of the tube, cooling the absorption liquid with the cooling water in the tube, and removing the heat generated during absorption. Absorbs refrigerant vapor from the absorber and becomes a dilute absorber.
In a solution heat exchanger (plate type), the efficiency of the cycle is increased by heat exchange between the dilute solution and the concentrated solution. The hot water flowing into the generator tube heats the absorption liquid to evaporate the refrigerant and increase the concentration of the absorption liquid. The concentrated liquid concentrated in the generator is sent to the absorber through the solution heat exchanger.
Secondary absorber Cooling water flows through the tube, absorbing the refrigerant vapor by dispersing the absorption liquid on the surface of the tube, cooling the absorption liquid with the cooling water in the tube to remove the heat generated during absorption, and absorbing the refrigerant vapor from the secondary absorber to make it a dilute absorption liquid.
Auxiliary solution Heat exchanger (plate type) heat exchanges auxiliary auxiliary solution with auxiliary auxiliary solution to increase cycle efficiency. Condenser The cooling water from the secondary absorber passes through the tube and condenses the refrigerant vapor from the auxiliary generator into the refrigerant liquid.
Cold water flows into the evaporator tube and cold water is produced by the evaporation of the refrigerant on the tube surface.
Coolant flows into the absorber tube, absorbing the refrigerant vapor by dispersing the absorbent on the surface of the tube, cooling the absorption liquid with the cooling water in the tube, and removing the heat generated during absorption. Absorbs refrigerant vapor from the absorber and becomes a dilute absorber.
In a solution heat exchanger (plate type), the efficiency of the cycle is increased by heat exchange between the dilute solution and the concentrated solution. The hot water flowing into the generator tube heats the absorption liquid to evaporate the refrigerant and increase the concentration of the absorption liquid. The concentrated liquid concentrated in the generator is sent to the absorber through the solution heat exchanger.
Secondary absorber Cooling water flows through the tube, absorbing the refrigerant vapor by dispersing the absorption liquid on the surface of the tube, cooling the absorption liquid with the cooling water in the tube to remove the heat generated during absorption, and absorbing the refrigerant vapor from the secondary absorber to make it a dilute absorption liquid.
Auxiliary solution Heat exchanger (plate type) heat exchanges auxiliary auxiliary solution with auxiliary auxiliary solution to increase cycle efficiency. Condenser The cooling water from the secondary absorber passes through the tube and condenses the refrigerant vapor from the auxiliary generator into the refrigerant liquid.